2D examples¶
These examples require raw data which are automatically
downloaded from the source repository by the script
example_helper.py.
Please make sure that this script is present in the example
script folder.
Mie off-center cylinder¶
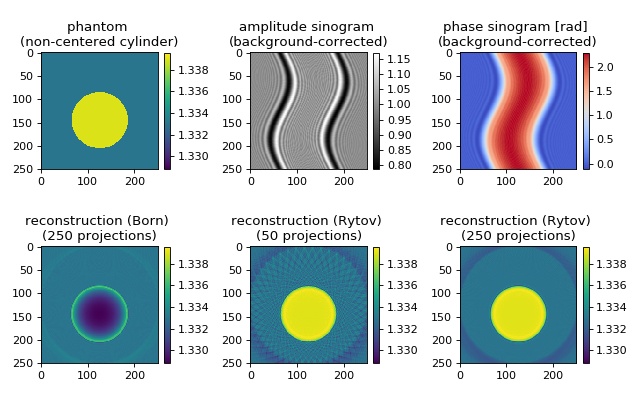
The in silico data set was created with the softare miefield. The data are 1D projections of an off-center cylinder of constant refractive index. The Born approximation is error-prone due to a relatively large radius of the cylinder (30 wavelengths) and a refractive index difference of 0.006 between cylinder and surrounding medium. The reconstruction of the refractive index with the Rytov approximation is in good agreement with the input data. When only 50 projections are used for the reconstruction, artifacts appear. These vanish when more projections are used for the reconstruction.
backprop_from_mie_2d_cylinder_offcenter.py
1import matplotlib.pylab as plt
2import numpy as np
3
4import odtbrain as odt
5
6from example_helper import load_data
7
8
9# simulation data
10sino, angles, cfg = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
11 f_sino_imag="sino_imag.txt",
12 f_sino_real="sino_real.txt",
13 f_angles="mie_angles.txt",
14 f_info="mie_info.txt")
15A, size = sino.shape
16
17# background sinogram computed with Mie theory
18# miefield.GetSinogramCylinderRotation(radius, nmed, nmed, lD, lC, size, A,res)
19u0 = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
20 f_sino_imag="u0_imag.txt",
21 f_sino_real="u0_real.txt")
22# create 2d array
23u0 = np.tile(u0, size).reshape(A, size).transpose()
24
25# background field necessary to compute initial born field
26# u0_single = mie.GetFieldCylinder(radius, nmed, nmed, lD, size, res)
27u0_single = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
28 f_sino_imag="u0_single_imag.txt",
29 f_sino_real="u0_single_real.txt")
30
31print("Example: Backpropagation from 2D Mie simulations")
32print("Refractive index of medium:", cfg["nmed"])
33print("Measurement position from object center:", cfg["lD"])
34print("Wavelength sampling:", cfg["res"])
35print("Performing backpropagation.")
36
37# Set measurement parameters
38# Compute scattered field from cylinder
39radius = cfg["radius"] # wavelengths
40nmed = cfg["nmed"]
41ncyl = cfg["ncyl"]
42
43lD = cfg["lD"] # measurement distance in wavelengths
44lC = cfg["lC"] # displacement from center of image
45size = cfg["size"]
46res = cfg["res"] # px/wavelengths
47A = cfg["A"] # number of projections
48
49x = np.arange(size) - size / 2
50X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, x)
51rad_px = radius * res
52phantom = np.array(((Y - lC * res)**2 + X**2) < rad_px**2,
53 dtype=np.float) * (ncyl - nmed) + nmed
54
55# Born
56u_sinB = (sino / u0 * u0_single - u0_single) # fake born
57fB = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinB, angles, res, nmed, lD * res)
58nB = odt.odt_to_ri(fB, res, nmed)
59
60# Rytov
61u_sinR = odt.sinogram_as_rytov(sino / u0)
62fR = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinR, angles, res, nmed, lD * res)
63nR = odt.odt_to_ri(fR, res, nmed)
64
65# Rytov 50
66u_sinR50 = odt.sinogram_as_rytov((sino / u0)[::5, :])
67fR50 = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinR50, angles[::5], res, nmed, lD * res)
68nR50 = odt.odt_to_ri(fR50, res, nmed)
69
70# Plot sinogram phase and amplitude
71ph = odt.sinogram_as_radon(sino / u0)
72
73am = np.abs(sino / u0)
74
75# prepare plot
76vmin = np.min(np.array([phantom, nB.real, nR50.real, nR.real]))
77vmax = np.max(np.array([phantom, nB.real, nR50.real, nR.real]))
78
79fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(8, 5))
80axes = np.array(axes).flatten()
81
82phantommap = axes[0].imshow(phantom, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
83axes[0].set_title("phantom \n(non-centered cylinder)")
84
85amplmap = axes[1].imshow(am, cmap="gray")
86axes[1].set_title("amplitude sinogram \n(background-corrected)")
87
88phasemap = axes[2].imshow(ph, cmap="coolwarm")
89axes[2].set_title("phase sinogram [rad] \n(background-corrected)")
90
91axes[3].imshow(nB.real, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
92axes[3].set_title("reconstruction (Born) \n(250 projections)")
93
94axes[4].imshow(nR50.real, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
95axes[4].set_title("reconstruction (Rytov) \n(50 projections)")
96
97axes[5].imshow(nR.real, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
98axes[5].set_title("reconstruction (Rytov) \n(250 projections)")
99
100# color bars
101cbkwargs = {"fraction": 0.045}
102plt.colorbar(phantommap, ax=axes[0], **cbkwargs)
103plt.colorbar(amplmap, ax=axes[1], **cbkwargs)
104plt.colorbar(phasemap, ax=axes[2], **cbkwargs)
105plt.colorbar(phantommap, ax=axes[3], **cbkwargs)
106plt.colorbar(phantommap, ax=axes[4], **cbkwargs)
107plt.colorbar(phantommap, ax=axes[5], **cbkwargs)
108
109plt.tight_layout()
110plt.show()
Mie cylinder with unevenly spaced angles¶
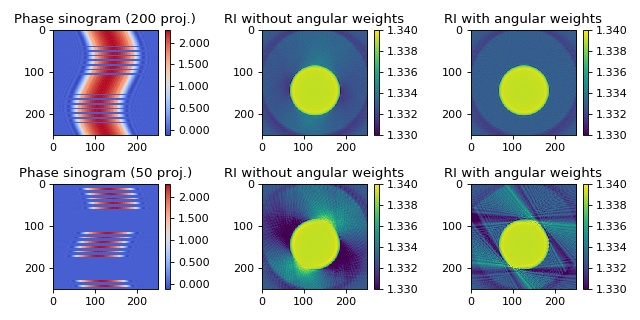
Angular weighting can significantly improve reconstruction quality when the angular projections are sampled at non-equidistant intervals [TPM81]. The in silico data set was created with the softare miefield. The data are 1D projections of a non-centered cylinder of constant refractive index 1.339 embedded in water with refractive index 1.333. The first column shows the used sinograms (missing angles are displayed as zeros) that were created from the original sinogram with 250 projections. The second column shows the reconstruction without angular weights and the third column shows the reconstruction with angular weights. The keyword argument weight_angles was introduced in version 0.1.1.
backprop_from_mie_2d_weights_angles.py
1import matplotlib.pylab as plt
2import numpy as np
3import unwrap
4
5import odtbrain as odt
6
7from example_helper import load_data
8
9
10sino, angles, cfg = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
11 f_angles="mie_angles.txt",
12 f_sino_real="sino_real.txt",
13 f_sino_imag="sino_imag.txt",
14 f_info="mie_info.txt")
15A, size = sino.shape
16
17# background sinogram computed with Mie theory
18# miefield.GetSinogramCylinderRotation(radius, nmed, nmed, lD, lC, size, A,res)
19u0 = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
20 f_sino_imag="u0_imag.txt",
21 f_sino_real="u0_real.txt")
22# create 2d array
23u0 = np.tile(u0, size).reshape(A, size).transpose()
24
25# background field necessary to compute initial born field
26# u0_single = mie.GetFieldCylinder(radius, nmed, nmed, lD, size, res)
27u0_single = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
28 f_sino_imag="u0_single_imag.txt",
29 f_sino_real="u0_single_real.txt")
30
31
32print("Example: Backpropagation from 2D FDTD simulations")
33print("Refractive index of medium:", cfg["nmed"])
34print("Measurement position from object center:", cfg["lD"])
35print("Wavelength sampling:", cfg["res"])
36print("Performing backpropagation.")
37
38# Set measurement parameters
39# Compute scattered field from cylinder
40radius = cfg["radius"] # wavelengths
41nmed = cfg["nmed"]
42ncyl = cfg["ncyl"]
43
44lD = cfg["lD"] # measurement distance in wavelengths
45lC = cfg["lC"] # displacement from center of image
46size = cfg["size"]
47res = cfg["res"] # px/wavelengths
48A = cfg["A"] # number of projections
49
50x = np.arange(size) - size / 2.0
51X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, x)
52rad_px = radius * res
53phantom = np.array(((Y - lC * res)**2 + X**2) < rad_px **
54 2, dtype=np.float) * (ncyl - nmed) + nmed
55
56u_sinR = odt.sinogram_as_rytov(sino / u0)
57
58# Rytov 200 projections
59# remove 50 projections from total of 250 projections
60remove200 = np.argsort(angles % .0002)[:50]
61angles200 = np.delete(angles, remove200, axis=0)
62u_sinR200 = np.delete(u_sinR, remove200, axis=0)
63ph200 = unwrap.unwrap(np.angle(sino / u0))
64ph200[remove200] = 0
65
66fR200 = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinR200, angles200, res, nmed, lD*res)
67nR200 = odt.odt_to_ri(fR200, res, nmed)
68fR200nw = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinR200, angles200, res, nmed, lD*res,
69 weight_angles=False)
70nR200nw = odt.odt_to_ri(fR200nw, res, nmed)
71
72# Rytov 50 projections
73remove50 = np.argsort(angles % .0002)[:200]
74angles50 = np.delete(angles, remove50, axis=0)
75u_sinR50 = np.delete(u_sinR, remove50, axis=0)
76ph50 = unwrap.unwrap(np.angle(sino / u0))
77ph50[remove50] = 0
78
79fR50 = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinR50, angles50, res, nmed, lD*res)
80nR50 = odt.odt_to_ri(fR50, res, nmed)
81fR50nw = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinR50, angles50, res, nmed, lD*res,
82 weight_angles=False)
83nR50nw = odt.odt_to_ri(fR50nw, res, nmed)
84
85# prepare plot
86kw_ri = {"vmin": 1.330,
87 "vmax": 1.340}
88
89kw_ph = {"vmin": np.min(np.array([ph200, ph50])),
90 "vmax": np.max(np.array([ph200, ph50])),
91 "cmap": "coolwarm"}
92
93fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(8, 4))
94axes = np.array(axes).flatten()
95
96phmap = axes[0].imshow(ph200, **kw_ph)
97axes[0].set_title("Phase sinogram (200 proj.)")
98
99rimap = axes[1].imshow(nR200nw.real, **kw_ri)
100axes[1].set_title("RI without angular weights")
101
102axes[2].imshow(nR200.real, **kw_ri)
103axes[2].set_title("RI with angular weights")
104
105axes[3].imshow(ph50, **kw_ph)
106axes[3].set_title("Phase sinogram (50 proj.)")
107
108axes[4].imshow(nR50nw.real, **kw_ri)
109axes[4].set_title("RI without angular weights")
110
111axes[5].imshow(nR50.real, **kw_ri)
112axes[5].set_title("RI with angular weights")
113
114# color bars
115cbkwargs = {"fraction": 0.045,
116 "format": "%.3f"}
117plt.colorbar(phmap, ax=axes[0], **cbkwargs)
118plt.colorbar(phmap, ax=axes[3], **cbkwargs)
119plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[1], **cbkwargs)
120plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[2], **cbkwargs)
121plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[5], **cbkwargs)
122plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[4], **cbkwargs)
123
124plt.tight_layout()
125plt.show()
Mie cylinder with incomplete angular coverage¶
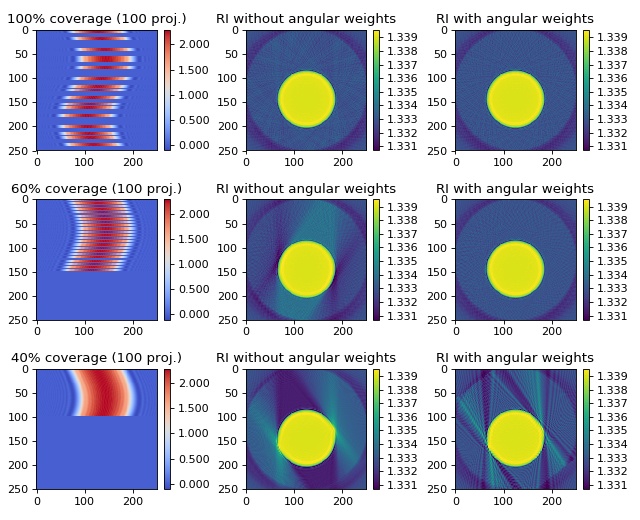
This example illustrates how the backpropagation algorithm of ODTbrain handles incomplete angular coverage. All examples use 100 projections at 100%, 60%, and 40% total angular coverage. The keyword argument weight_angles that invokes angular weighting is set to True by default. The in silico data set was created with the softare miefield. The data are 1D projections of a non-centered cylinder of constant refractive index 1.339 embedded in water with refractive index 1.333. The first column shows the used sinograms (missing angles are displayed as zeros) that were created from the original sinogram with 250 projections. The second column shows the reconstruction without angular weights and the third column shows the reconstruction with angular weights. The keyword argument weight_angles was introduced in version 0.1.1.
A 180 degree coverage results in a good reconstruction of the object. Angular weighting as implemented in the backpropagation algorithm of ODTbrain automatically addresses uneven and incomplete angular coverage.
backprop_from_mie_2d_incomplete_coverage.py
1import matplotlib.pylab as plt
2import numpy as np
3
4import odtbrain as odt
5
6from example_helper import load_data
7
8sino, angles, cfg = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
9 f_angles="mie_angles.txt",
10 f_sino_real="sino_real.txt",
11 f_sino_imag="sino_imag.txt",
12 f_info="mie_info.txt")
13A, size = sino.shape
14
15# background sinogram computed with Mie theory
16# miefield.GetSinogramCylinderRotation(radius, nmed, nmed, lD, lC, size, A,res)
17u0 = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
18 f_sino_imag="u0_imag.txt",
19 f_sino_real="u0_real.txt")
20# create 2d array
21u0 = np.tile(u0, size).reshape(A, size).transpose()
22
23# background field necessary to compute initial born field
24# u0_single = mie.GetFieldCylinder(radius, nmed, nmed, lD, size, res)
25u0_single = load_data("mie_2d_noncentered_cylinder_A250_R2.zip",
26 f_sino_imag="u0_single_imag.txt",
27 f_sino_real="u0_single_real.txt")
28
29print("Example: Backpropagation from 2D FDTD simulations")
30print("Refractive index of medium:", cfg["nmed"])
31print("Measurement position from object center:", cfg["lD"])
32print("Wavelength sampling:", cfg["res"])
33print("Performing backpropagation.")
34
35# Set measurement parameters
36# Compute scattered field from cylinder
37radius = cfg["radius"] # wavelengths
38nmed = cfg["nmed"]
39ncyl = cfg["ncyl"]
40
41lD = cfg["lD"] # measurement distance in wavelengths
42lC = cfg["lC"] # displacement from center of image
43size = cfg["size"]
44res = cfg["res"] # px/wavelengths
45A = cfg["A"] # number of projections
46
47x = np.arange(size) - size / 2.0
48X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, x)
49rad_px = radius * res
50phantom = np.array(((Y - lC * res)**2 + X**2) < rad_px **
51 2, dtype=np.float) * (ncyl - nmed) + nmed
52
53u_sinR = odt.sinogram_as_rytov(sino / u0)
54
55# Rytov 100 projections evenly distributed
56removeeven = np.argsort(angles % .002)[:150]
57angleseven = np.delete(angles, removeeven, axis=0)
58u_sinReven = np.delete(u_sinR, removeeven, axis=0)
59pheven = odt.sinogram_as_radon(sino / u0)
60pheven[removeeven] = 0
61
62fReven = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinReven, angleseven, res, nmed, lD * res)
63nReven = odt.odt_to_ri(fReven, res, nmed)
64fRevennw = odt.backpropagate_2d(
65 u_sinReven, angleseven, res, nmed, lD * res, weight_angles=False)
66nRevennw = odt.odt_to_ri(fRevennw, res, nmed)
67
68# Rytov 100 projections more than 180
69removemiss = 249 - \
70 np.concatenate((np.arange(100), 100 + np.arange(150)[::3]))
71anglesmiss = np.delete(angles, removemiss, axis=0)
72u_sinRmiss = np.delete(u_sinR, removemiss, axis=0)
73phmiss = odt.sinogram_as_radon(sino / u0)
74phmiss[removemiss] = 0
75
76fRmiss = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinRmiss, anglesmiss, res, nmed, lD * res)
77nRmiss = odt.odt_to_ri(fRmiss, res, nmed)
78fRmissnw = odt.backpropagate_2d(
79 u_sinRmiss, anglesmiss, res, nmed, lD * res, weight_angles=False)
80nRmissnw = odt.odt_to_ri(fRmissnw, res, nmed)
81
82# Rytov 100 projections less than 180
83removebad = 249 - np.arange(150)
84anglesbad = np.delete(angles, removebad, axis=0)
85u_sinRbad = np.delete(u_sinR, removebad, axis=0)
86phbad = odt.sinogram_as_radon(sino / u0)
87phbad[removebad] = 0
88
89fRbad = odt.backpropagate_2d(u_sinRbad, anglesbad, res, nmed, lD * res)
90nRbad = odt.odt_to_ri(fRbad, res, nmed)
91fRbadnw = odt.backpropagate_2d(
92 u_sinRbad, anglesbad, res, nmed, lD * res, weight_angles=False)
93nRbadnw = odt.odt_to_ri(fRbadnw, res, nmed)
94
95# prepare plot
96kw_ri = {"vmin": np.min(np.array([phantom, nRmiss.real, nReven.real])),
97 "vmax": np.max(np.array([phantom, nRmiss.real, nReven.real]))}
98
99kw_ph = {"vmin": np.min(np.array([pheven, phmiss])),
100 "vmax": np.max(np.array([pheven, phmiss])),
101 "cmap": "coolwarm"}
102
103fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=(8, 6.5))
104
105axes[0, 0].set_title("100% coverage ({} proj.)".format(angleseven.shape[0]))
106phmap = axes[0, 0].imshow(pheven, **kw_ph)
107
108axes[0, 1].set_title("RI without angular weights")
109rimap = axes[0, 1].imshow(nRevennw.real, **kw_ri)
110
111axes[0, 2].set_title("RI with angular weights")
112rimap = axes[0, 2].imshow(nReven.real, **kw_ri)
113
114axes[1, 0].set_title("60% coverage ({} proj.)".format(anglesmiss.shape[0]))
115axes[1, 0].imshow(phmiss, **kw_ph)
116
117axes[1, 1].set_title("RI without angular weights")
118axes[1, 1].imshow(nRmissnw.real, **kw_ri)
119
120axes[1, 2].set_title("RI with angular weights")
121axes[1, 2].imshow(nRmiss.real, **kw_ri)
122
123axes[2, 0].set_title("40% coverage ({} proj.)".format(anglesbad.shape[0]))
124axes[2, 0].imshow(phbad, **kw_ph)
125
126axes[2, 1].set_title("RI without angular weights")
127axes[2, 1].imshow(nRbadnw.real, **kw_ri)
128
129axes[2, 2].set_title("RI with angular weights")
130axes[2, 2].imshow(nRbad.real, **kw_ri)
131
132# color bars
133cbkwargs = {"fraction": 0.045,
134 "format": "%.3f"}
135plt.colorbar(phmap, ax=axes[0, 0], **cbkwargs)
136plt.colorbar(phmap, ax=axes[1, 0], **cbkwargs)
137plt.colorbar(phmap, ax=axes[2, 0], **cbkwargs)
138plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[0, 1], **cbkwargs)
139plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[1, 1], **cbkwargs)
140plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[2, 1], **cbkwargs)
141plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[0, 2], **cbkwargs)
142plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[1, 2], **cbkwargs)
143plt.colorbar(rimap, ax=axes[2, 2], **cbkwargs)
144
145plt.tight_layout()
146plt.show()
FDTD cell phantom¶
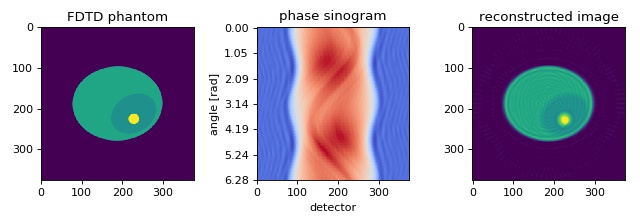
The in silico data set was created with the FDTD software meep. The data are 1D projections of a 2D refractive index phantom. The reconstruction of the refractive index with the Rytov approximation is in good agreement with the phantom that was used in the simulation.
1import matplotlib.pylab as plt
2import numpy as np
3import odtbrain as odt
4
5from example_helper import load_data
6
7
8sino, angles, phantom, cfg = load_data("fdtd_2d_sino_A100_R13.zip",
9 f_angles="fdtd_angles.txt",
10 f_sino_imag="fdtd_imag.txt",
11 f_sino_real="fdtd_real.txt",
12 f_info="fdtd_info.txt",
13 f_phantom="fdtd_phantom.txt",
14 )
15
16print("Example: Backpropagation from 2D FDTD simulations")
17print("Refractive index of medium:", cfg["nm"])
18print("Measurement position from object center:", cfg["lD"])
19print("Wavelength sampling:", cfg["res"])
20print("Performing backpropagation.")
21
22# Apply the Rytov approximation
23sino_rytov = odt.sinogram_as_rytov(sino)
24
25# perform backpropagation to obtain object function f
26f = odt.backpropagate_2d(uSin=sino_rytov,
27 angles=angles,
28 res=cfg["res"],
29 nm=cfg["nm"],
30 lD=cfg["lD"] * cfg["res"]
31 )
32
33# compute refractive index n from object function
34n = odt.odt_to_ri(f, res=cfg["res"], nm=cfg["nm"])
35
36# compare phantom and reconstruction in plot
37fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(8, 2.8))
38
39axes[0].set_title("FDTD phantom")
40axes[0].imshow(phantom, vmin=phantom.min(), vmax=phantom.max())
41sino_phase = np.unwrap(np.angle(sino), axis=1)
42
43axes[1].set_title("phase sinogram")
44axes[1].imshow(sino_phase, vmin=sino_phase.min(), vmax=sino_phase.max(),
45 aspect=sino.shape[1] / sino.shape[0],
46 cmap="coolwarm")
47axes[1].set_xlabel("detector")
48axes[1].set_ylabel("angle [rad]")
49
50axes[2].set_title("reconstructed image")
51axes[2].imshow(n.real, vmin=phantom.min(), vmax=phantom.max())
52
53# set y ticks for sinogram
54labels = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, len(axes[1].get_yticks()))
55labels = ["{:.2f}".format(i) for i in labels]
56axes[1].set_yticks(np.linspace(0, len(angles), len(labels)))
57axes[1].set_yticklabels(labels)
58
59plt.tight_layout()
60plt.show()